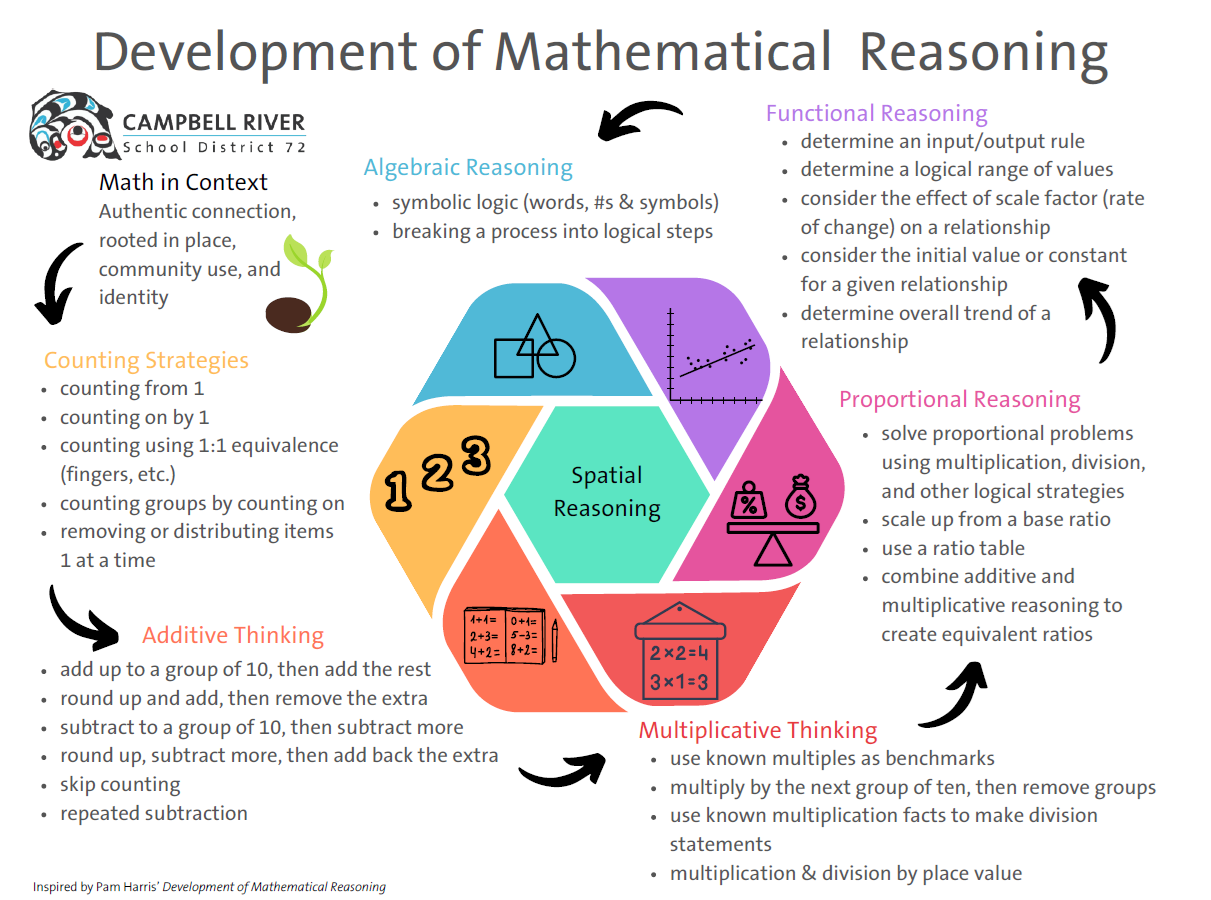
Intro to Numeracy
Numerate citizens have opportunities to solve a variety of problems using logic and reasoning. Numeracy instruction in SD72 includes real-world problem solving of in-context problems that are age appropriate and locally relevant. Exploring, developing, and celebrating both traditional and modern ways of integrating mathematical knowledge into our lives connects us to each other, to the past, and to the future.
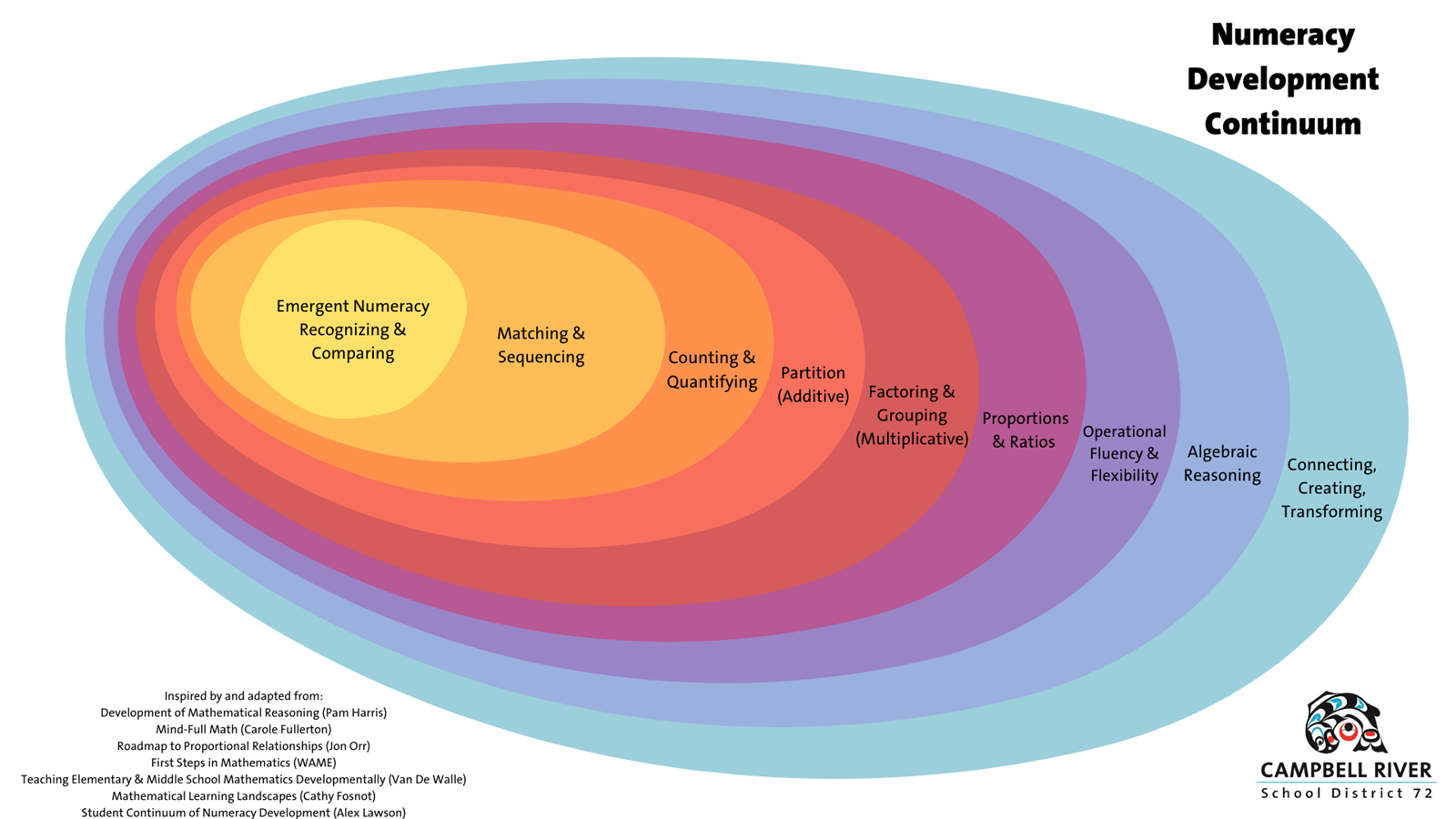
In addition to progressing through these stages of conceptual numeracy, students also develop their spatial and statistical reasoning throughout their learning trajectory.
| Description | Document | |
| 1 | Tri-axial weave model combining curricular content, competencies, and First Peoples' Principles of Learning | Interweaving Math Content, Competencies, & Culture (Diagram) |
| 2 | Nested shell model of numeracy development | Numeracy Development Continuum (Diagram) |
| 3 | Outlines the stages of mathematical reasoning from counting to algebraic reasoning | Development of Mathematical Reasoning (Diagram) |
| 4 | Rubric-style, multi-grade tables that show the progression of foundational numeracy and operational fluency (K to 9). | Foundational Numeracy and Operational Fluency Trajectories |
| 5 | Table mapping the BC curricular competencies for math K-9 in terms of depth of knowledge (Planning and assessment resource) | Depth of Knowledge and Curricular Competencies Table (11 x 17) |
| 6 | Matrix (Table) relating depth of knowledge (DOK) and cognitive rigor in math | Webb / Hess DOK and Cognitive Rigor Table |
| 7 | "Myself in Math" Self-Reflection (template) | BC Core Competencies in Math (Self-Reflection) |
| 8 | Checklist for self-reporting learning habits in math class | Mathematical Habits of Mind (Self-Assessment) |
| 9 | Templates for Number Sense and Operations SNAP assessments (Grade 2 to 9) | SNAP Assessments (Grade 2 to 9) |